$75,000 After Tax in Ontario: How Much Do You Have to Earn to Bring Home $75k in Ontario?
You need to earn a gross employment income of around $105,000 to take home $75,000 in Ontario. So, does the difference between gross and net pay go only into the government’s coffers? The short answer is no. You get direct benefits through paybacks in addition to indirect benefits like good infrastructure, public health insurance, and medical facilities.
Let's take a closer look at what some of these direct and indirect benefits and paybacks consist of in the Province of Ontario.
Benefits Paid Back to You (Directly)
One of the deductions from gross pay is CPP (Canada Pension Plan). A pension plan deducts a small amount from employment income and pays you monthly allowances after retirement. If you are earning $75,000 after tax in Ontario, the maximum CPP deduction is $3,500 a year ($292 a month).
Another deduction is EI (Employment Insurance) which serves as a premium paid to buy an insurance policy. This claim benefits you in the event that you lose your job, provided that you meet the eligibility criteria. Continuing with our example, employers deduct an amount of $953 a year ($80 a month).
Indirect Benefits
You are paying $16,635 and $8,056 as federal and provincial income tax on your gross pay to arrive at $75,000 after tax in Ontario. Do not forget to avail tax credits to reduce tax liability. A tax credit is a direct reduction in tax liability.
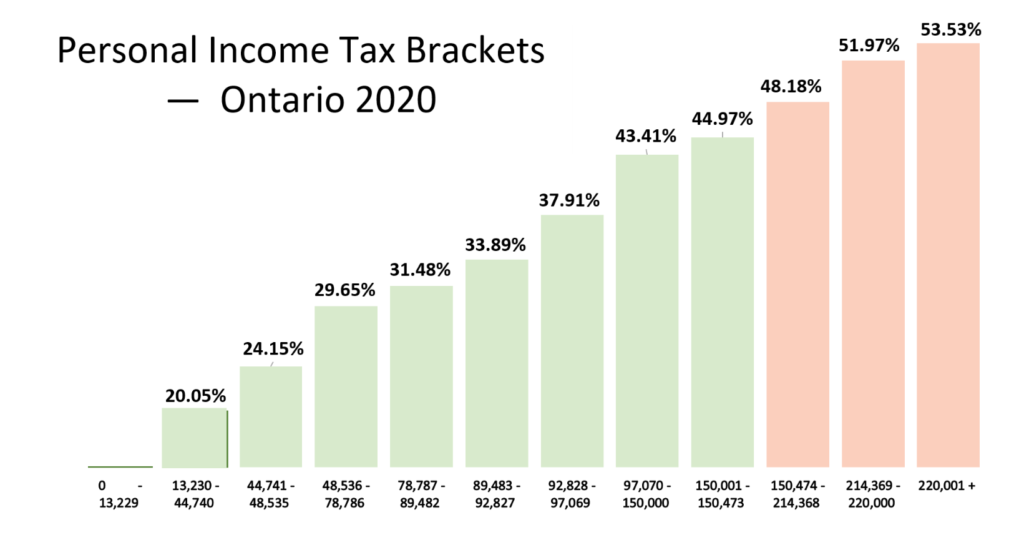
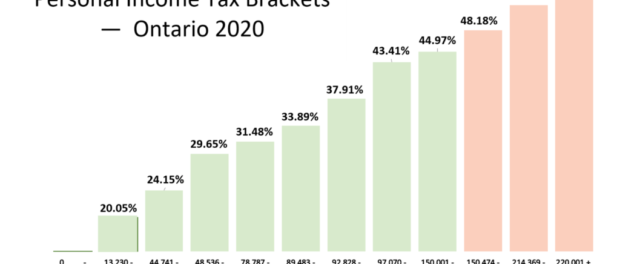
Ontario charges progressive tax. The more your income is, the higher you pay in taxes as a percentage of your earnings. See below an example from 2020:
Source: MD Tax
Reducing Tax Liability – Tax Credits
Donations paid to registered charities are one way to claim the tax credit. You need to retain the supporting documents to produce in case of a tax inquiry.
Paying an eligible tuition fee to a recognized educational institute may help you to claim up to 15% of the fee paid as a tax credit. Any unclaimed fees (due to unavailability of income) can be carried forward for adjustment from your income in later years.
Medical expenses paid for oneself, one's spouse, or one’s children act as a tax credit too. You can claim a higher amount of this tax credit if medical expenses are deducted by the spouse with a lower Net Income for Tax Purposes. Lower income means more room to claim a higher tax credit.
Non-Employment Ways of Earning Income
So far, we discussed making $75,000 after tax in Ontario only from an employee’s perspective. There can be other active and passive income sources as well.
We commit our skills through rendering services or delivering goods to earn “active income”. Passive sources involve setting aside capital to earn income on our behalf, including rental income, interest proceeds, and royalties. Keep in mind the two sources of income until the end of this article.
Active Business Income
Earning income through running an active business is the most common alternative to employment income. Businesses benefit from a wide variety of expenses available for deduction from revenue, unlike employment income where deduction options are just a few.
It’s difficult to estimate the gross revenue that could make you earn $75,000 after tax in Ontario as a business owner.The nature of one’s expenses play a vital role. Higher expenses mean lower tax liability, but also lower net earnings. Some expenses are not recognized by tax authorities and added back. They include penalties, fines, federal political contributions, or 50% of one’s total entertainment expenses.
The 2022 federal tax rates for business income range from 9% to 15%. The Government of Ontario imposes a further tax of 12.2% to 26.5%. You will get a lower rate (9% federal and 12.2% provincial) if you can claim a SBD (Small Business Deduction).
SBD incentivizes small businesses with lower taxation rates. If you have annual revenue of up to $500,000, your business might fall into this category.
You can work independently as, for example, a health service provider, musician, writer, or real estate agent. You can avail SBD deduction if the above income conditions are met.
Property Income
Earning interest from investments, dividends, and rental income are the most common property income types. Here you do not commit significant time and labor.
Earning interest income locally will charge you tax at the same rate as the salaried class. You will pay WHT (Withholding Tax) if interest is earned outside Canada. You probably do not need to pay an additional tax to the Canadian government if a tax treaty exists.
Understanding dividend income is a bit trickier. You might earn dividends as a business owner or in the capacity of an individual shareholder.
You can transfer yourself all the after-tax income from the business or earn it as a shareholder. Both options are considered for earning dividend income. But don't worry, because you pay the same amount of tax under both options thanks to the concept of integration.
“Integration” ensures you are not paying double tax on dividends. You pay double tax when you include dividends in the return as taxable income, that is already taxed earlier as business profits.
Dividends earned from foreign companies are grossed up and included in income. Grossing up means dividing the net foreign dividend received by the withholding tax rate. You arrive at the gross foreign dividend earned, that you later include in the return. You then get a foreign tax credit to compensate for the foreign tax paid.
In a nutshell, it is not straightforward to estimate the gross property income you need to get $75,000 after tax in Ontario. We explained the taxability of different sources of income. It all boils down to the expenses you are deducting from your income.
A Word of Advice
Earning ‘active’ income in any form gives you the room to invest in an RRSP (Registered Retirement Savings Plan) or TFSA (Tax-Free Savings Account). Each year you get a certain amount, based on your active income that you can invest tax-free.
Investments made to your RRSP can be deducted from your income. The result is a lower tax liability.
Investments in listed securities have gained public attention in the last two decades. Recent years have taken a shift towards cryptocurrencies. But you cannot deny the consistent importance of holding a physical asset whose value is evergreen.
If you cannot afford to buy sky-rocketing priced real estate, sealing a deal to buy gold or silver coins is a win-win alternative. You can buy as much as you want, without the fear of losing significant investment value due to a sudden stock market crash.
Invest wisely!

Will Your Retirement Weather the Next Financial Crisis?
Gold has been used as an inflation hedge and a way to preserve wealth for millennia. We partnered with Silver Gold Bull, Canada's top-rated gold company (with over 280,000 five-star reviews), to offer Canadians a low-cost and tax-advantaged way to buy gold and silver through an RRSP/TFSA or another retirement plan.
Request More Info
Website: www.SilverGoldBull.ca
Speak to an Expert: (877) 707-4707
Copyright 2026 Gold RRSP - Helping Canadians invest in physical bullion for retirement